|
Project Introduction:
In its regular Traffic and Market Data report, which provides insights into current trends, Ericsson forecasts a 10-fold increase in mobile data traffic by 2016. According to the report, mobile broadband subscriptions will reach almost 5 billion in 2016, up from the expected 900 million by the end of 2011.That would represent 60 percent year-on-year growth, at the same time as the data consumed by smart phone users is surging. Total smart phone traffic is expected to triple during 2011. Across all devices, internet access will continue to drive mobile traffic development and mobile data traffic is expected to grow by nearly 60 percent per year between 2011 and 2016, mainly driven by video.
As operators look to support broader video services more efficiently, switched broadcast services will play a key role in enabling intelligence at the network edge. They achieve this by implementing a control plane with a control function for video-on-demand services or switched broadcastservices whereby the network is queried for availability of the required resources in order to deliver the service type to a subscriber. The network either confirms or refuses the resources to deliver the service, and provisions the network accordingly. This allows operators to distribute content into different areas in the network. An example is where popular content is located on servers in the distribution hub. When high demand content becomes available, like a blockbuster movie, operators could pre-populate servers at the network edge so that more subscribers can access the content consuming fewer network resources and less core bandwidth. This gives operators a more efficient network which can scale with subscriber demand and offer more cost-effective digital video services.
By definition the network edge is where a network of computers process and store data for delivery close to the final destination. Because storage, processing and delivery are done closer to the edge, service reliability and quality is increased overall and local network problems are less likely to have global side effects. The challenge for service providers is how to efficiently scale the network edge and deliver the perfect mobile and video experiences in a competitive world while tightly managing CAPEX and OPEX.
One flexible and scalable approach to resolve these challenges is to deploy networking elements at the network edge based on ATCA blades using only Intel Architecture processors. Today’s edge infrastructure is built on multiple technologies making it difficult to power manage and costly to scale, complicating the addition of new services. Building an edge infrastructure based on one common architecture enables consolidation of services and packet processing workloads onto a single processor architecture, reducing network complexity and simplifying management through common tools, application software and platform consistency.
Together with Intel virtualization technology a single architecture introduces flexibility to handle changing service demand by re-provisioning cores, blades or systems as needed. Videos can be migrated from node to node from the core to the edge, without service interruption, in reaction to changing demand. Performance and energy consumption can be easily scaled based on workload demands. Deploying Advantech’s Intel based networking systems at the service edge can also help improve customer QoE while creating potential for new service revenue models. By delivering the highest demand video content from the edge to the consumers, latency and jitter can be reduced which improves the viewing experience an opens up opportunities for differentiated managed services to generate new revenue streams.
Flexible, telecom-approved processing nodes are key elements required when constructing an SEN platform. Adherence to open standards linked to the availability of the latest and most powerful IA silicon makes AdvancedTCA the ideal architectural choice. Advantech can provide multiple choices when it comes to matching processing blades to the needs of the specific network element. Single or dual Intel Xeon based boards are available such as Advantech’s MIC-5322 and MIC-5332 which can be populated with 2, 4, 6 or 8 core processors delivering on the flexibility to create multiple SEN variants.
12 and 16-Core Intel® Xeon® 5600 / E5-2600 Series ATCA Blades for Service Edge Node (SEN) Integration
MIC-5322 DUAL INTEL® XEON® 5600 SERIES PROCESSOR BLADE
The MIC-5322 is a dual processor Intel® Xeon® 5500/5600-based ATCA blade. It enables the highest performance available in ATCA form factor with 12-cores and 24-threads of processing power, low DDR3 memory latency, fast PCI Express 2.0 and accelerated virtualization. The Intel 82599 10 GbE controller plays a key role in end-to-end network performance and throughput, including a 5 Gbps PCI Express 2.0 interface to improve the entire data path as well as multi-core optimized queue support. For fast and secure database applications, the blade supports up to 48 GB of triple channel DDR3 with ECC. The flexibility of the Intel® Xeon® 5500/5600 Series allows tremendous upgradeability, scalability and cost efficiency options with two, four or six-core processors fully supported.
 |
 |
Two 2, 4 or 6-Core Intel® Xeon® 5500 or 5600 processors |
 |
Intel® 5520 IOH36D/ICH10R server class chipset |
 |
6 DDR3 VLP DIMMs up to 48 GB with ECC support |
 |
Two XAUI ports on Fabric interface |
 |
Two 1000BASE-T ports on Base interface |
 |
Two 1000BASE-T front panel ports |
 |
Two USB2.0 front panel ports |
 |
Fully managed, hot swappable RTM |
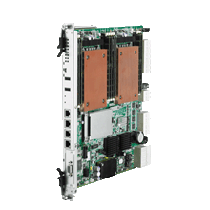
MIC-5332 DUAL INTEL® XEON® E5-2600 SERIES PROCESSOR BLADE
Advantech’s MIC-5332 is a dual processor ATCA blade based on the Intel® Xeon® E5-2600 series processors. It enables the highest performance available in ATCA form factor with up to 16 cores and 32 threads of processing power, fast PCI Express gen. 3 lanes running at up to 8Gbps, and best in class virtualization support. Two QPI interfaces between the CPUs improve memory and I/O access throughput and latencies when one processor needs to access resources hosted by the other socket. With four DDR3 DIMMs per socket in a quad channel design running up to 1600MT/s, the MIC-5332 not only offers superior memory bandwidth over 3-channel designs, but can also support memory densities up 256GB using latest LR DIMM technology. It outperforms previous generation dual socket designs while keeping similar thermal characteristics with balanced airflow resistance.
 |
Two Intel® Xeon® E5-2600 Processors |
 |
 |
Intel C600 Series PCH server class chipset with integrated SAS controller |
 |
8 DDR3 VLP DIMMs up to 256 GB with ECC support |
 |
Up to four XAUI ports on Fabric interface |
 |
Two 1000BASE-T ports on Base interface |
 |
Three 1000BASE-T front panel ports |
 |
One Fabric Mezzanine Module support with front I/O support (type II) |
 |
Two CFast / one 2.5" SSD storage Device |
 |
Fully managed, hot swappable RTM |
| |
|
|